
For this $f$, the range is the set of non-negative real numbers while the codomain is the set of all real numbers. What is range in math Range in math is the difference between the least and greatest value in a set of data. Since $f(x)$ will always be non-negative, the number $-3$ is in the codomain of $f$, but it is not in the range, as there is no input of $x$ for which $f(x)=-3$. It is possible there are objects in the codomain for which there are no inputs for which the function will output that object.įor example, we could define a function $f: \R \to \R$ as $f(x)=x^2$. All we know is that the range must be a subset of the codomain, so the range must be a subset (possibly the whole set) of the real numbers. But, without knowing what the function $f$ is, we cannot determine what its outputs are so we cannot what its range is.
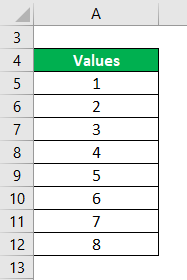
From this notation, we know that the set of all inputs (the domain) of $f$ isi the set of all real numbers and the set of all possible inputs (the codomain) is also the set of all real numbers. Range is a fundamental concept in mathematics that refers to the set of all possible output values of a function. In the function machine metaphor, the range is the set of objects that actually come out of the machine when you feed it all the inputs.įor example, when we use the function notation $f: \R \to \R$, we mean that $f$ is a function from the real numbers to the real numbers. Polynomials (Definition, Types and Examples). The larger variance and standard deviation in Dataset B further demonstrates that Dataset B is more dispersed than Dataset A.The range of a function is the set of outputs the function achieves when it is applied to its whole set of outputs. Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to. The population variance \(\sigma^2\) (pronounced sigma squared) of a discrete set of numbers is expressed by the following formula: In a normal distribution, about 68% of the values are within one standard deviation either side of the mean and about 95% of the scores are within two standard deviations of the mean. The standard deviation of a normal distribution enables us to calculate confidence intervals. To find the range, subtract the lowest number from the biggest number. Therefore, if all values of a dataset are the same, the standard deviation and variance are zero. The range is the difference between the biggest and the smallest number. The midrange is the average of the largest and smallest data points. The smaller the variance and standard deviation, the more the mean value is indicative of the whole dataset. The Range (Estadistika) - Wikipedia, ang malayang ensiklopedya is the difference between the largest and smallest data points in a set of numerical data. Where a dataset is more dispersed, values are spread further away from the mean, leading to a larger variance and standard deviation.

In datasets with a small spread all values are very close to the mean, resulting in a small variance and standard deviation. They summarise how close each observed data value is to the mean value. The variance and the standard deviation are measures of the spread of the data around the mean.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
